Nature conservation in Arunachal Pradesh

Arunachal Pradesh in the Eastern Himalayas of India is among the 200 globally important ecoregions. It is also considered as one of the eighteen “biodiversity hotspots” in the world. An estimation that over 5000 species of flowering plants are found (of both vascular and non-vascular origin) here, out of which, 238 are endemic to the state. The state is rich in agro-biodiversity and has been a center of origin for a number of crop plant species. Orchids are often associated as the “Jewels of Arunachal Pradesh”, more than 500 of its varieties can be found here. The state has more than 500 species of fauna and shelters four major cats namely tiger, leopard, clouded leopard, snow leopard and also rare lesser feline species like the Golden Cat and Marbled Cat. It also covers an amazingly rich variety of avifauna with over 650 bird species.
Ecological Hotspot:
Arunachal Pradesh is one of the world’s top “ecological hotspots” having a vast range of flora & fauna species and ecosystem diversity. The state covers the easternmost part of the country, and has been known as one of the biodiversity hotspots in the world. The Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve (DDBR) located in the Reserved Forests spreads in West Siang, Upper Siang and Dibang Valley of Arunachal Pradesh and is the largest and most biodiverse spot.
Problems Resulting in Biodiversity Loss:
Conservation biologists warn that 25% of total life forms could become extinct during the next twenty to thirty years; the causes for loss of species are numerous, most importantly: the fragmentation of natural habitats, deforestation, Jhum Cultivation, timber felling, hunting, soil erosion, encroachment problem and urbanization. Each community exercises control over the natural resources within their inhabited area and uses the resources for shelter, cultivation, food, daily multifarious uses and other human activities.
Measures:
Taking the vulnerability of living being from natural calamities and indiscreet exploitation of natural resources, measures have been suggested to Geographers to develop strategies and geospatial technologies for conservation of the flora, fauna and natural environment.
Pakke-Paga Hornbill Festival – the only conservation festival has been declared as the state festival to promote conservation of nature.
Source: Wikipedia
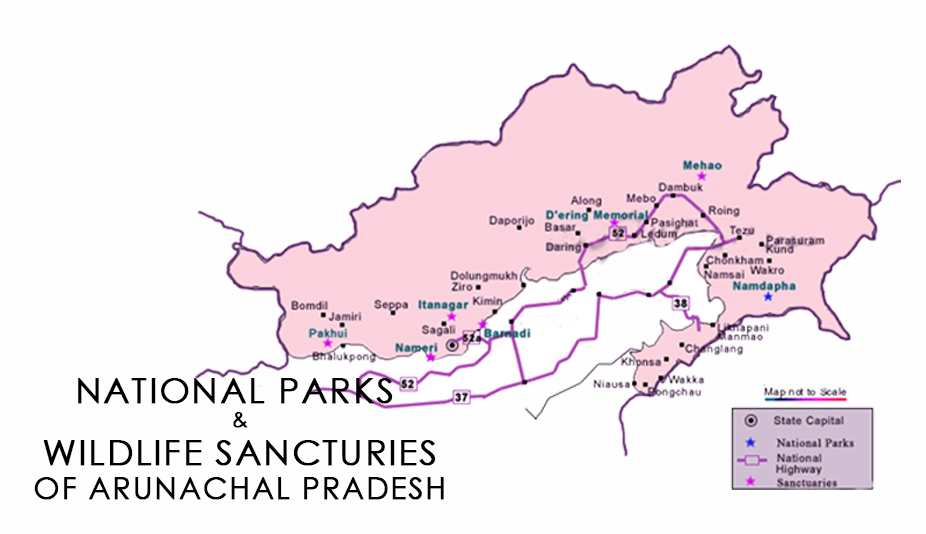
Various in situ, as well as ex-situ measures like the establishment of arboretums, sanctuaries, parks and reserve forests, protected areas etc. 2 national parks, 1 orchid sanctuary and 7 wildlife sanctuaries have been protected to save the loss of biodiversity.
These are:
- Talle Wildlife Sanctuary(PAN)
- DihangDibang Biosphere Reserve
- Eagle Nest Wildlife Sanctuary
- Namdapha Tiger Reserve
- Mouling National Park
- Sessa Orchid Sanctuary
- Pakke Wildlife Sanctuary
- Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Itanagar Wildlife Sanctuary
 Source: Facebook Page: Eco-Tourism Society of Arunachal Pradesh
Source: Facebook Page: Eco-Tourism Society of Arunachal Pradesh
Ecotourism: has been initiated by the people as a measure for sustainable development. Arunachal is an ideal location for nature lovers and adventurers as here one can find the perfect opportunity to relax in the midst of picturesque hills, snowy mist, famous monasteries, unexplored passes and tranquil lakes all of which come together to form some of the prettiest locations in the largest state of North East India which is encircled on three sides by Bhutan, China and Myanmar. The state is not only rich in natural beauty but also has a diverse culture within the many communities who live here. Apatani Plateau Initiative and Ziro and Tangsa Community Conservation Reserve Initiative, Changlang District have been major initiatives executed by Association for Conservation and Tourism in the state. They aim at the sole motive of creating a friendly environment for tribals and making conserving the pristine environment and soulful tourism.
Community Ecotourism: The local communities get direct livelihood benefits from a homestay operation, local cuisine, transport, bird-watching ponds and hides, bird guide services, selling of local products and souvenirs and cultural program performances. They are also actively involved in various bird and nature conservation activities.
 Source: http://thegreenpastures.com
Source: http://thegreenpastures.com
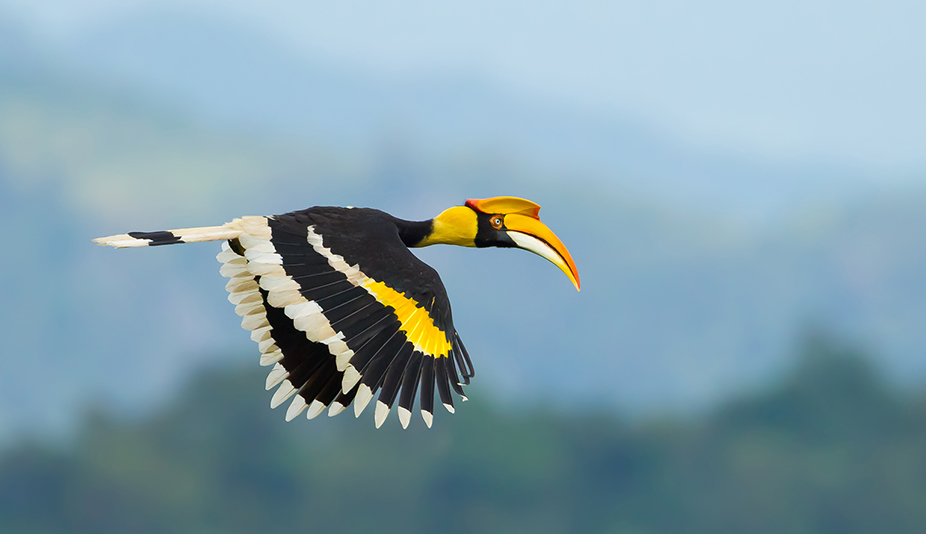
Birdwatching Ecotourism or Avitourism is a form of nature-based ecotourism that mainly focuses on observing and identifying birds in their natural habitats. Birdwatchers are mostly conservation-minded responsible eco-tourists who have respect for wildlife and natural habitats. Considering the rich diversity of birds and the presence of important bird areas in Arunachal Pradesh, there is ample opportunity for the development of bird-watching ecotourism in the state. This can provide alternative livelihood opportunity to the local community and also reduce pressure on the forest and natural resources and ultimately help in conservation of biodiversity.
 Source: Facebook Page: Eco-Tourism Society of Arunachal Pradesh
Source: Facebook Page: Eco-Tourism Society of Arunachal Pradesh
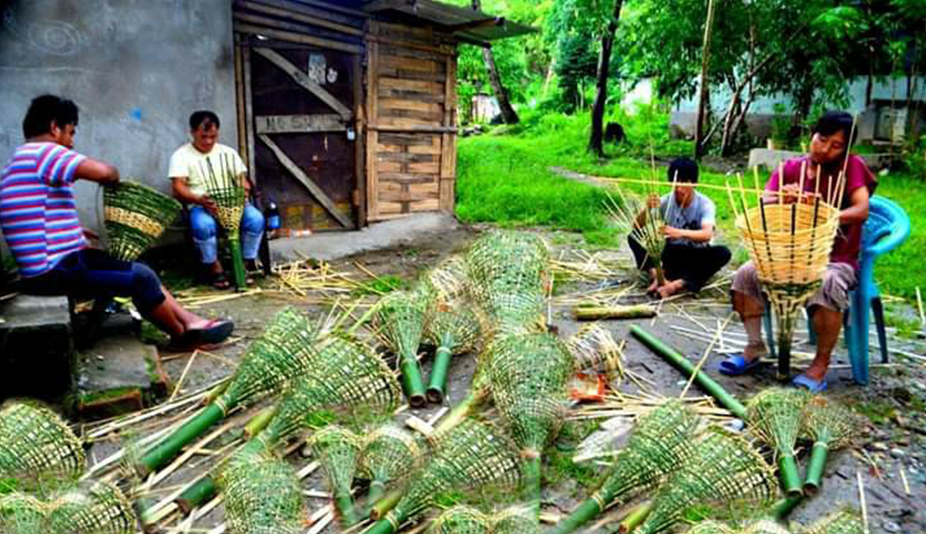
Eco-friendly Initiatives: Many communities, NGOs, schools and colleges have been taking an active part in keeping Arunachal clean and green. People have been making and using eco-friendly dustbins, utensils and household items etc. in order to sell or for self-use. These are low costing pocket-friendly items which can be bought in stalls or street markets. Using eco-friendly items helps save nature in effective ways since it is biodegradable and harmless for human health.
Lastly, it needs to be expressed that responsible travel needs to be promoted for sustainable tourism which can be initiated by minimum destruction, environmental growth, adventure and preaching sustainable ways of living on the planet. We need to promote the tourism industry so that an alternative source of income can be provided and at the same time bring an end to the consumption of various resources of the region for monetary benefits.


Total Comments - 0